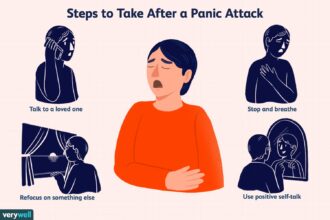
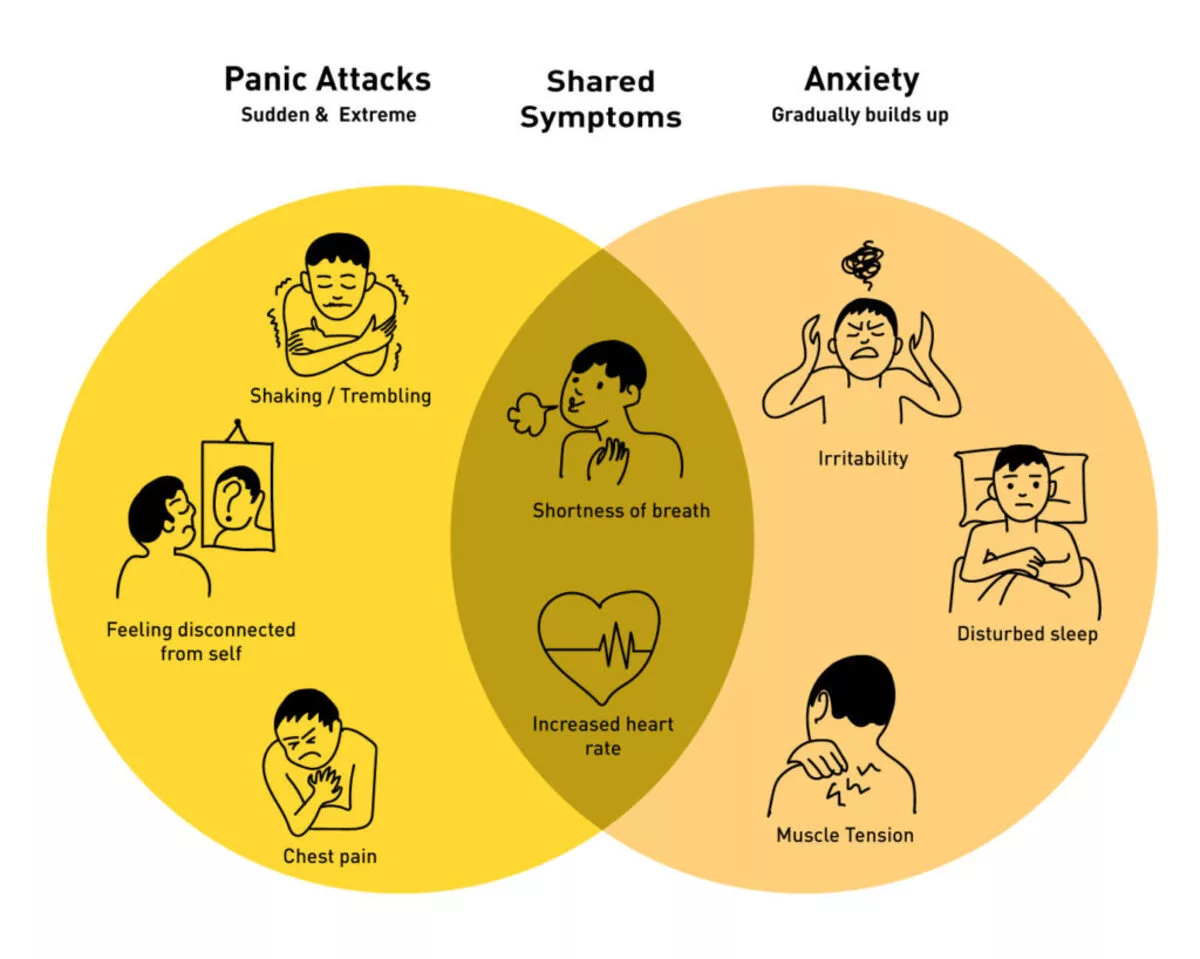
In this blog post, we will explore the intricate relationship between anxiety and our mental and physical health, shedding light on the hidden consequences that often go unnoticed.
So grab a cup of tea, find a comfortable spot, and let’s delve into this important topic that touches the lives of so many.
Definition and brief overview of anxiety
Anxiety is a normal and often healthy emotion that everyone experiences from time to time.
It is a feeling of unease, such as worry or fear, that can be mild or severe.
Anxiety becomes a problem when it is persistent, intense, and interferes with daily activities.
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive anxiety, fear, or apprehension.
These disorders can cause significant distress and impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning.
There are several types of anxiety disorders, including:
- generalized anxiety disorder
- panic disorder
- social anxiety disorder
- and specific phobias.
Each type of anxiety disorder has its own set of symptoms and diagnostic criteria.
Treatment for anxiety disorders usually includes a combination of psychotherapy, medications, or a combination of both.
Lifestyle changes, such as:
- regular exercise
- adequate sleep
- and stress reduction techniques
can also help manage anxiety symptoms.
Mental Health Effects of Anxiety
Anxiety can have various mental health effects, including:
- Increased risk of developing mood disorders
Chronic anxiety can increase the risk of developing mood disorders such as depression and bipolar disorder.
This is because anxiety can lead to changes in brain chemistry and structure, which can affect mood regulation.
- Depression: Anxiety and depression often co-occur. Chronic anxiety can lead to depression, and vice versa.
- Bipolar disorder: Anxiety is also a common symptom of bipolar disorder, and people with bipolar disorder often experience anxiety during both manic and depressive episodes.
- Difficulty in maintaining focus and concentration:
Anxiety can make it difficult to concentrate on tasks, which can affect work or school performance.
- Impact on cognitive function
Chronic anxiety can also affect cognitive function, including:
- Memory: Anxiety can affect both short-term and long-term memory, making it difficult to remember important details.
- Decision-making skills: Anxiety can make it difficult to make decisions, especially in situations where the outcome is uncertain.
- Social implications and the potential for social anxiety disorder
Anxiety can have social implications, making it difficult to interact with others and form relationships. For some people, chronic anxiety can lead to social anxiety disorder, which is characterized by an intense fear of social situations.
- Effects on self-esteem and self-confidence
Chronic anxiety can erode self-esteem and self-confidence, leading to feelings of inadequacy and worthlessness.
This can make it difficult to pursue goals and engage in activities that would otherwise be enjoyable.

Physical Health Effects of Anxiety
Anxiety can also have various physical health effects, including:
- Chronic stress and its consequences:
Anxiety can cause chronic stress, which can have negative effects on physical health, including:
- Impact on immune system functioning: Chronic stress can suppress the immune system, making it more difficult to fight off illnesses and infections.
- Increased vulnerability to illnesses and infections: Prolonged stress can increase the risk of developing illnesses and infections, such as the common cold, flu, and other viral infections.
- Disruption of sleep patterns and insomnia:
It can cause disruptions in sleep patterns, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. This can lead to sleep deprivation, which can affect overall health and wellbeing.
- Effects on cardiovascular health:
Chronic anxiety can have negative effects on cardiovascular health, including:
- Increased risk of heart disease: Chronic anxiety can increase the risk of developing heart disease, including coronary artery disease and heart attacks.
- Blood pressure fluctuations: Anxiety can cause fluctuations in blood pressure, which can put additional strain on the cardiovascular system.
- Gastrointestinal issues and digestive disorders:
Anxiety can also affect the digestive system, leading to:
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Anxiety can worsen symptoms of IBS, which is a common digestive disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
- Acidity and ulcers: Chronic anxiety can also increase the production of stomach acid, which can lead to acidity and ulcers.
Read more: Psychological causes of anxiety

Effects of Anxiety on Relationships
Anxiety can also have various effects on relationships, including:
- Difficulty in forming and maintaining intimate relationships:
Anxiety can make it difficult to form and maintain intimate relationships.
People with anxiety may have a fear of being rejected or abandoned, which can lead to avoidance of intimate relationships.
- Impact on family dynamics:
Anxiety can also affect family dynamics, causing tension and conflict.
For example, a person with anxiety may be overly protective of their loved ones or have difficulty trusting others.
- Strained friendships and social interactions:
Anxiety can also strain friendships and social interactions.
People with anxiety may avoid social situations or have difficulty engaging in conversation, which can lead to social isolation and loneliness.
- Professional implications and the potential for career setbacks:
Anxiety can also have professional implications, including the potential for career setbacks.
People with anxiety may have difficulty performing well at work, interacting with colleagues, and making decisions, which can affect their job performance and career advancement.
Overall, anxiety can have a significant impact on relationships, including intimate relationships, family dynamics, friendships, and professional relationships.
It is important for people with anxiety to seek help and support in order to improve their relationships and overall quality of life.

Coping Strategies and Treatment Options for Anxiety
There are several coping strategies and treatment options available for anxiety, including:
- Psychotherapy and counseling:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety.
- It is a highly effective treatment for anxiety disorders.
- Exposure therapy: Exposure therapy involves gradually exposing individuals to anxiety-provoking situations in a safe and controlled environment.
- This can help them learn to manage their anxiety and reduce their fear response.
- Medication and pharmacological interventions:
- Anti-anxiety medications: Anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines, can help reduce anxiety symptoms.
- However, these medications can be habit-forming and have other potential side effects.
- Antidepressants and mood stabilizers: Antidepressants and mood stabilizers can be effective in treating anxiety disorders, especially when combined with therapy.
- These medications can take several weeks to start working and may have side effects.
- Lifestyle modifications and self-care practices:
- Regular exercise and physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower anxiety levels and improve overall mental health.
- Stress management techniques (e.g., meditation, deep breathing exercises): Learning and practicing stress management techniques can help individuals manage their anxiety symptoms and reduce stress levels.
- Healthy eating habits and a balanced diet: Eating a healthy, balanced diet can help improve overall physical and mental health, which can in turn reduce anxiety symptoms.
It is important to note that the most effective treatment for anxiety often involves a combination of these strategies.
It is recommended that individuals with anxiety seek professional help from a mental health provider to determine the best course of treatment for their individual needs.
Conclusion
Many people face issues with anxiety and stress in their lives, but there are many available treatment options and strategies that can help overcome these problems.
Through psychotherapy, medication, lifestyle modifications, and self-care practices, individuals can access the necessary support to alleviate anxiety and improve their quality of life.
When anxiety is diagnosed on a long-term basis, individuals should seek the necessary help from qualified healthcare providers and mental health specialists.
With determination and hard work, individuals can achieve mental comfort and success in life.