In this insightful blog post, we will explore some of the key factors that contribute to this debilitating condition, from early childhood experiences to genetic predisposition, and shed light on the complex interplay between nature and nurture that underpins anxiety disorders.
So, whether you’re seeking to understand your own anxiety or looking to support a loved one, read on to discover the inner workings of this complex and fascinating condition.
What is anxiety
Anxiety is a normal and often helpful human emotion that is experienced in response to stress or perceived threats.
It is a feeling of unease, worry, or fear that can range from mild to severe and can be triggered by a variety of situations or circumstances, such as public speaking, financial difficulties, or health concerns.
However, when anxiety becomes excessive, persistent, and interferes with daily life, it can be considered a mental health disorder.
Anxiety disorders are a group of conditions characterized by excessive and persistent feelings of anxiety and fear.
Some common types of anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias.
Symptoms of anxiety can include physical sensations such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, and shortness of breath, as well as psychological symptoms such as excessive worry, restlessness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
Treatment for anxiety disorders may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both, and can be highly effective in helping individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Causes of anxiety
The causes of anxiety can be complex and multifactorial, and may vary from person to person. Here are some common factors that can contribute to the development of anxiety:
- Genetics: Anxiety disorders can run in families, indicating a genetic component to the condition.
- Brain chemistry: Neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin and dopamine, play a role in regulating mood and anxiety. Imbalances in these chemicals may contribute to the development of anxiety disorders.
- Environmental factors: Traumatic or stressful life events, such as abuse, neglect, or the death of a loved one, may trigger the onset of anxiety symptoms.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, heart disease, or chronic pain, may contribute to the development of anxiety.
- Substance use/withdrawal: Use of drugs or alcohol, or withdrawal from them, can trigger anxiety symptoms.
- Personality traits: Some people may have a naturally anxious temperament, which can increase their risk of developing an anxiety disorder.
- Cognitive factors: Negative thought patterns and beliefs, such as catastrophic thinking or a tendency to overestimate the likelihood of danger, can contribute to anxiety.
It’s important to note that anxiety is often the result of a combination of these factors, and that not everyone who experiences these factors develops an anxiety disorder.

Symptoms of anxiety
Anxiety can present itself with a wide range of symptoms, both physical and psychological. Here are some common symptoms of anxiety:
- Excessive worry or fear about everyday situations or events.
- Restlessness or feeling keyed up or on edge.
- Muscle tension, trembling, or shaking.
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations.
- Sweating or hot flashes.
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Nausea, stomach upset, or diarrhea.
- Difficulty concentrating or feeling easily distracted.
- Sleep disturbances, such as difficulty falling or staying asleep, or having restless, unsatisfying sleep.
- Avoidance of situations that trigger anxiety.
- Panic attacks, which are sudden and intense episodes of anxiety that may include symptoms such as chest pain, dizziness, and a sense of impending doom.
- Irritability or feeling easily agitated.
- Feeling constantly on guard or hypervigilant.
- Obsessive or compulsive behaviors that are difficult to control.
It’s important to note that everyone experiences anxiety differently, and not everyone with anxiety will experience all of these symptoms. Additionally, some of these symptoms can be caused by other medical conditions, so it’s important to seek a professional evaluation if you are experiencing any of these symptoms.
How to deal with anxiety
There are many strategies that can help individuals manage and reduce anxiety symptoms. Here are some tips for dealing with anxiety:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can all be effective ways to calm the body and mind.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress and anxiety, as well as improve mood and overall health.
- Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can exacerbate anxiety symptoms, so it’s important to get enough restful sleep each night.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol: Stimulants such as caffeine and alcohol can increase anxiety symptoms, so it’s best to avoid or limit them.
- Challenge negative thoughts: Negative thought patterns and beliefs can contribute to anxiety, so it can be helpful to challenge and reframe them in a more positive light.
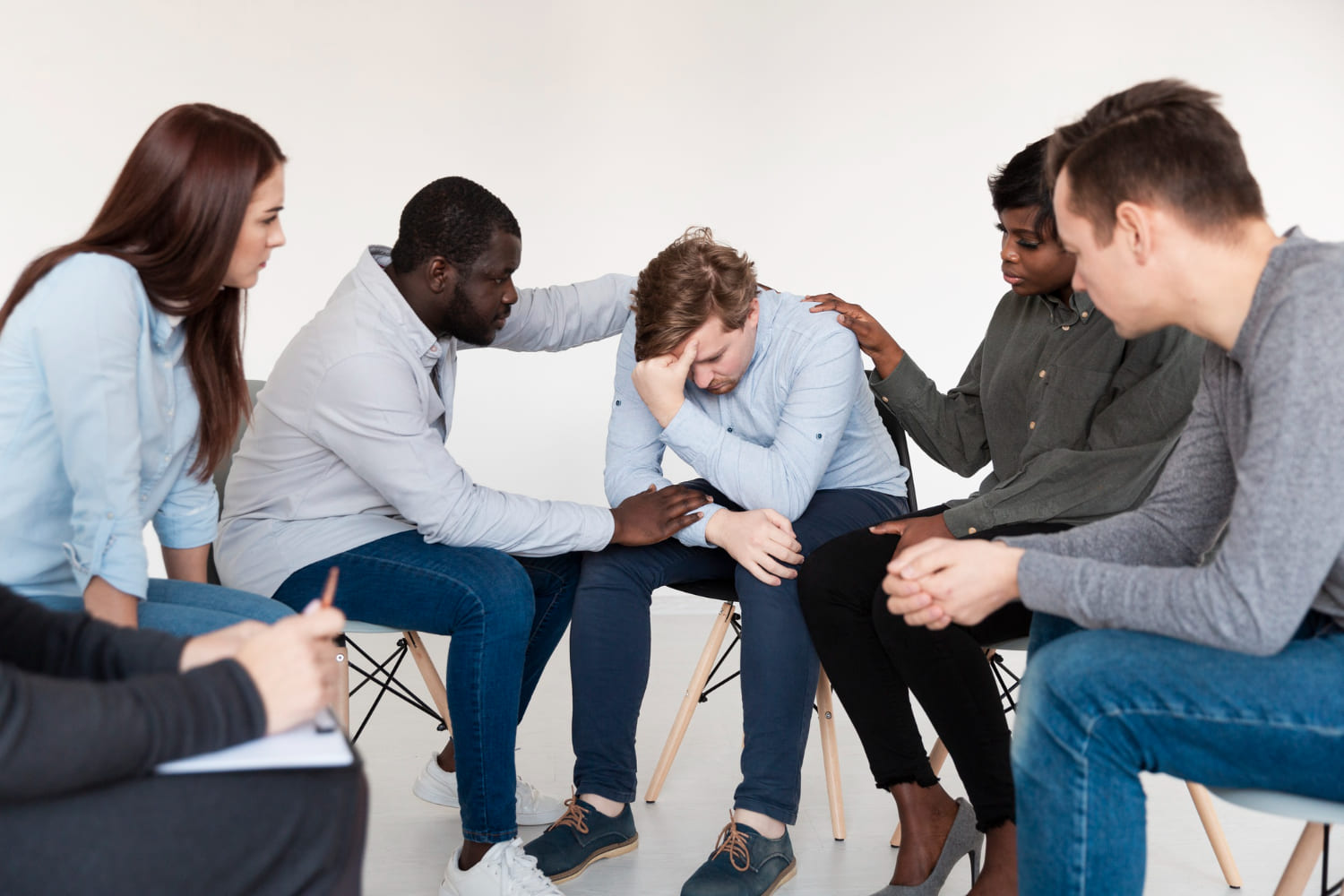
- Seek support: Talking to a trusted friend or family member, joining a support group, or seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide valuable support and guidance.
- Practice self-care: Engage in activities that bring you pleasure and relaxation, such as reading a book, taking a bath, or spending time in nature.
- Consider medication: In some cases, medication may be recommended as part of a treatment plan for anxiety. Talk to your healthcare provider to determine if medication is a good option for you.
It’s important to remember that everyone’s experience with anxiety is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Experimenting with different strategies can help you find what works best for you. Additionally, seeking professional help can provide personalized support and guidance in managing anxiety symptoms.
Anxiety disorder
Anxiety Disorder is a broad term that refers to a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive and persistent feelings of anxiety, worry, and fear. While the term “Anxiety Disorder” is used to describe the group of conditions as a whole, each specific type of anxiety disorder has its own name and diagnostic criteria
Types of anxiety disorders
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Excessive and persistent worry about everyday life events and situations.
- Panic Disorder: Recurrent panic attacks, which are sudden and intense periods of overwhelming fear and physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, sweating, and shortness of breath.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Intense fear of social situations, such as public speaking, meeting new people, or attending social events.
- Specific Phobias: Intense fear or avoidance of a specific object or situation, such as heights, spiders, or flying.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Repeated, unwanted thoughts or obsessions, accompanied by repetitive behaviors or compulsions, such as excessive cleaning or checking.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Anxiety and distress following a traumatic event, such as a natural disaster, combat, or assault.

Generalized anxiety disorder treatment
Treatment for GAD typically involves a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Here are some common treatments for GAD:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This type of therapy helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety. CBT can also help individuals learn coping strategies and relaxation techniques.
- Medication: Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can be effective in treating GAD. Your healthcare provider can determine if medication is a good option for you.
- Relaxation Techniques: Deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can all be effective ways to calm the body and mind.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress and anxiety, as well as improve mood and overall health.
- Lifestyle Changes: Eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and limiting caffeine and alcohol can all help reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group or talking to others who have experienced similar symptoms can provide valuable support and guidance.
It’s important to remember that everyone’s experience with GAD is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Seeking professional help can provide personalized support and guidance in managing GAD symptoms and improving quality of life.
Conclusion
anxiety disorder is a common and often debilitating mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While anxiety is a normal and sometimes helpful human emotion, excessive and persistent anxiety can interfere with daily life and lead to a range of physical and psychological symptoms. Fortunately, there are effective treatments available for anxiety disorders, including therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Seeking professional help early on can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
With the right support and treatment, individuals with anxiety disorders can learn to manage their symptoms and live fulfilling and meaningful lives.